注意
转到末尾 以下载完整的示例代码。
逐步输出中间结果¶
我们重用示例 转换带有 ColumnTransformer 的管道 中的示例,并逐步输出中间结果。转换后的模型很可能由于未正确实现的自定义转换器而产生不同的输出或失败。一种方法是查看 ONNX 图中每个节点的输出。
创建和训练一个复杂的管道¶
我们重用在示例 带有混合类型的 Column Transformer 中实现的管道。有一个改动,因为 ONNX-ML Imputer 不支持字符串类型。这不能作为最终 ONNX 管道的一部分,必须移除。请查看下面以 --- 开头的注释。
import skl2onnx
import onnx
import sklearn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
from onnx.tools.net_drawer import GetPydotGraph, GetOpNodeProducer
from skl2onnx.helpers.onnx_helper import select_model_inputs_outputs
from skl2onnx.helpers.onnx_helper import save_onnx_model
from skl2onnx.helpers.onnx_helper import enumerate_model_node_outputs
from skl2onnx.helpers.onnx_helper import load_onnx_model
import numpy
import onnxruntime as rt
from skl2onnx import convert_sklearn
import pprint
from skl2onnx.common.data_types import (
FloatTensorType,
StringTensorType,
Int64TensorType,
)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
titanic_url = (
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/amueller/"
"scipy-2017-sklearn/091d371/notebooks/datasets/titanic3.csv"
)
data = pd.read_csv(titanic_url)
X = data.drop("survived", axis=1)
y = data["survived"]
# SimpleImputer on string is not available
# for string in ONNX-ML specifications.
# So we do it beforehand.
for cat in ["embarked", "sex", "pclass"]:
X[cat].fillna("missing", inplace=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
numeric_features = ["age", "fare"]
numeric_transformer = Pipeline(
steps=[("imputer", SimpleImputer(strategy="median")), ("scaler", StandardScaler())]
)
categorical_features = ["embarked", "sex", "pclass"]
categorical_transformer = Pipeline(
steps=[
# --- SimpleImputer is not available for strings in ONNX-ML specifications.
# ('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy='constant', fill_value='missing')),
("onehot", OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown="ignore"))
]
)
preprocessor = ColumnTransformer(
transformers=[
("num", numeric_transformer, numeric_features),
("cat", categorical_transformer, categorical_features),
]
)
clf = Pipeline(
steps=[
("preprocessor", preprocessor),
("classifier", LogisticRegression(solver="lbfgs")),
]
)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
定义 ONNX 图的输入¶
sklearn-onnx 不知道用于训练模型的特征,但它需要知道哪个特征具有哪个名称。我们只是重用数据帧的列定义。
print(X_train.dtypes)
pclass int64
name object
sex object
age float64
sibsp int64
parch int64
ticket object
fare float64
cabin object
embarked object
boat object
body float64
home.dest object
dtype: object
转换后。
def convert_dataframe_schema(df, drop=None):
inputs = []
for k, v in zip(df.columns, df.dtypes):
if drop is not None and k in drop:
continue
if v == "int64":
t = Int64TensorType([None, 1])
elif v == "float64":
t = FloatTensorType([None, 1])
else:
t = StringTensorType([None, 1])
inputs.append((k, t))
return inputs
inputs = convert_dataframe_schema(X_train)
pprint.pprint(inputs)
[('pclass', Int64TensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('name', StringTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('sex', StringTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('age', FloatTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('sibsp', Int64TensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('parch', Int64TensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('ticket', StringTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('fare', FloatTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('cabin', StringTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('embarked', StringTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('boat', StringTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('body', FloatTensorType(shape=[None, 1])),
('home.dest', StringTensorType(shape=[None, 1]))]
将单个列合并为向量不是计算预测的最有效方法。可以在将管道转换为图之前完成。
将管道转换为 ONNX¶
scikit-learn 在可能的情况下会进行隐式转换。sklearn-onnx 不会。OneHotEncoder 的 ONNX 版本必须应用于相同类型的列。
X_train["pclass"] = X_train["pclass"].astype(str)
X_test["pclass"] = X_test["pclass"].astype(str)
white_list = numeric_features + categorical_features
to_drop = [c for c in X_train.columns if c not in white_list]
inputs = convert_dataframe_schema(X_train, to_drop)
model_onnx = convert_sklearn(clf, "pipeline_titanic", inputs, target_opset=12)
# And save.
with open("pipeline_titanic.onnx", "wb") as f:
f.write(model_onnx.SerializeToString())
比较预测¶
最后一步,我们需要确保转换后的模型产生相同的预测、标签和概率。让我们从scikit-learn 开始。
print("predict", clf.predict(X_test[:5]))
print("predict_proba", clf.predict_proba(X_test[:1]))
predict [0 0 0 1 1]
predict_proba [[0.78796696 0.21203304]]
使用 onnxruntime 进行预测。我们需要删除已删除的列,并将双精度向量更改为单精度向量,因为 onnxruntime 不支持双精度浮点数。onnxruntime 不接受 dataframe。输入必须以字典列表的形式提供。最后一个细节是,每一列都被描述为单个列的矩阵,而不是真正的向量,这解释了最后一行中的reshape。
我们已准备好运行 onnxruntime。
predict [0 0 0 1 1]
predict_proba [{0: 0.5883165597915649, 1: 0.41168344020843506}]
计算中间输出¶
不幸的是,目前没有办法让 onnxruntime 检索中间节点的输出。我们需要修改 ONNX,然后再将其提供给 onnxruntime。让我们先看看中间输出的列表。
merged_columns
embarkedout
sexout
pclassout
concat_result
variable
variable2
variable1
transformed_column
label
probabilities
output_label
output_probability
很难确定哪个是什么,因为 ONNX 拥有比原始 scikit-learn 管道更多的运算符。 显示 ONNX 图 中的图有助于我们找到数值管道和文本管道的输出:variable1,variable2。让我们先看看数值管道。
num_onnx = select_model_inputs_outputs(model_onnx, "variable1")
save_onnx_model(num_onnx, "pipeline_titanic_numerical.onnx")
b'\x08\x07\x12\x08skl2onnx\x1a\x061.19.1"\x07ai.onnx(\x002\x00:\xcd\x03\n:\n\x03age\n\x04fare\x12\x0emerged_columns\x1a\x06Concat"\x06Concat*\x0b\n\x04axis\x18\x01\xa0\x01\x02:\x00\n}\n\x0emerged_columns\x12\x08variable\x1a\x07Imputer"\x07Imputer*#\n\x14imputed_value_floats=\x00\x00\xe0A=gDgA\xa0\x01\x06*\x1e\n\x14replaced_value_float\x15\x00\x00\xc0\x7f\xa0\x01\x01:\nai.onnx.ml\n^\n\x08variable\x12\tvariable1\x1a\x06Scaler"\x06Scaler*\x15\n\x06offset=\x17\xc8\xebA=<\t\x07B\xa0\x01\x06*\x14\n\x05scale=D)\x9e==\xe5j\x9e<\xa0\x01\x06:\nai.onnx.ml\x12\x10pipeline_titanic*\x1f\x08\x02\x10\x07:\x0b\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\x01\tB\x0cshape_tensorZ\x16\n\x06pclass\x12\x0c\n\n\x08\x08\x12\x06\n\x00\n\x02\x08\x01Z\x13\n\x03sex\x12\x0c\n\n\x08\x08\x12\x06\n\x00\n\x02\x08\x01Z\x13\n\x03age\x12\x0c\n\n\x08\x01\x12\x06\n\x00\n\x02\x08\x01Z\x14\n\x04fare\x12\x0c\n\n\x08\x01\x12\x06\n\x00\n\x02\x08\x01Z\x18\n\x08embarked\x12\x0c\n\n\x08\x08\x12\x06\n\x00\n\x02\x08\x01b\x0b\n\tvariable1B\x04\n\x00\x10\x0bB\x0e\n\nai.onnx.ml\x10\x01'
我们来计算数值特征。
numerical features [[0.4268576 9.254629 ]]
我们对文本特征也做同样的处理。
print(model_onnx)
text_onnx = select_model_inputs_outputs(model_onnx, "variable2")
save_onnx_model(text_onnx, "pipeline_titanic_textual.onnx")
sess = rt.InferenceSession(
"pipeline_titanic_textual.onnx", providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
numT = sess.run(None, inputs)
print("textual features", numT[0][:1])
ir_version: 7
producer_name: "skl2onnx"
producer_version: "1.19.1"
domain: "ai.onnx"
model_version: 0
doc_string: ""
graph {
node {
input: "age"
input: "fare"
output: "merged_columns"
name: "Concat"
op_type: "Concat"
attribute {
name: "axis"
i: 1
type: INT
}
domain: ""
}
node {
input: "embarked"
output: "embarkedout"
name: "OneHotEncoder"
op_type: "OneHotEncoder"
attribute {
name: "cats_strings"
strings: "C"
strings: "Q"
strings: "S"
strings: "missing"
type: STRINGS
}
attribute {
name: "zeros"
i: 1
type: INT
}
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
}
node {
input: "sex"
output: "sexout"
name: "OneHotEncoder1"
op_type: "OneHotEncoder"
attribute {
name: "cats_strings"
strings: "female"
strings: "male"
type: STRINGS
}
attribute {
name: "zeros"
i: 1
type: INT
}
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
}
node {
input: "pclass"
output: "pclassout"
name: "OneHotEncoder2"
op_type: "OneHotEncoder"
attribute {
name: "cats_strings"
strings: "1"
strings: "2"
strings: "3"
type: STRINGS
}
attribute {
name: "zeros"
i: 1
type: INT
}
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
}
node {
input: "embarkedout"
input: "sexout"
input: "pclassout"
output: "concat_result"
name: "Concat1"
op_type: "Concat"
attribute {
name: "axis"
i: -1
type: INT
}
domain: ""
}
node {
input: "merged_columns"
output: "variable"
name: "Imputer"
op_type: "Imputer"
attribute {
name: "imputed_value_floats"
floats: 28
floats: 14.4542
type: FLOATS
}
attribute {
name: "replaced_value_float"
f: nan
type: FLOAT
}
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
}
node {
input: "concat_result"
input: "shape_tensor"
output: "variable2"
name: "Reshape"
op_type: "Reshape"
domain: ""
}
node {
input: "variable"
output: "variable1"
name: "Scaler"
op_type: "Scaler"
attribute {
name: "offset"
floats: 29.4727
floats: 33.7590179
type: FLOATS
}
attribute {
name: "scale"
floats: 0.0772271454
floats: 0.0193380807
type: FLOATS
}
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
}
node {
input: "variable1"
input: "variable2"
output: "transformed_column"
name: "Concat2"
op_type: "Concat"
attribute {
name: "axis"
i: 1
type: INT
}
domain: ""
}
node {
input: "transformed_column"
output: "label"
output: "probabilities"
name: "LinearClassifier"
op_type: "LinearClassifier"
attribute {
name: "classlabels_ints"
ints: 0
ints: 1
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "coefficients"
floats: 0.359008849
floats: 0.0514151268
floats: -0.355432689
floats: 0.247025743
floats: 0.314346433
floats: -0.270904839
floats: -1.22721398
floats: 1.16224873
floats: -0.955703616
floats: -0.0454647
floats: 0.936203
floats: -0.359008849
floats: -0.0514151268
floats: 0.355432689
floats: -0.247025743
floats: -0.314346433
floats: 0.270904839
floats: 1.22721398
floats: -1.16224873
floats: 0.955703616
floats: 0.0454647
floats: -0.936203
type: FLOATS
}
attribute {
name: "intercepts"
floats: -0.123175517
floats: 0.123175517
type: FLOATS
}
attribute {
name: "multi_class"
i: 0
type: INT
}
attribute {
name: "post_transform"
s: "LOGISTIC"
type: STRING
}
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
}
node {
input: "label"
output: "output_label"
name: "Cast"
op_type: "Cast"
attribute {
name: "to"
i: 7
type: INT
}
domain: ""
}
node {
input: "probabilities"
output: "output_probability"
name: "ZipMap"
op_type: "ZipMap"
attribute {
name: "classlabels_int64s"
ints: 0
ints: 1
type: INTS
}
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
}
name: "pipeline_titanic"
initializer {
dims: 2
data_type: 7
int64_data: -1
int64_data: 9
name: "shape_tensor"
}
input {
name: "pclass"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 8
shape {
dim {
}
dim {
dim_value: 1
}
}
}
}
}
input {
name: "sex"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 8
shape {
dim {
}
dim {
dim_value: 1
}
}
}
}
}
input {
name: "age"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 1
shape {
dim {
}
dim {
dim_value: 1
}
}
}
}
}
input {
name: "fare"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 1
shape {
dim {
}
dim {
dim_value: 1
}
}
}
}
}
input {
name: "embarked"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 8
shape {
dim {
}
dim {
dim_value: 1
}
}
}
}
}
output {
name: "output_label"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 7
shape {
dim {
}
}
}
}
}
output {
name: "output_probability"
type {
sequence_type {
elem_type {
map_type {
key_type: 7
value_type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 1
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
opset_import {
domain: ""
version: 11
}
opset_import {
domain: "ai.onnx.ml"
version: 1
}
textual features [[1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0.]]
显示子 ONNX 图¶
最后,让我们看看两个子图。首先,数值管道。
pydot_graph = GetPydotGraph(
num_onnx.graph,
name=num_onnx.graph.name,
rankdir="TB",
node_producer=GetOpNodeProducer(
"docstring", color="yellow", fillcolor="yellow", style="filled"
),
)
pydot_graph.write_dot("pipeline_titanic_num.dot")
os.system("dot -O -Gdpi=300 -Tpng pipeline_titanic_num.dot")
image = plt.imread("pipeline_titanic_num.dot.png")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(40, 20))
ax.imshow(image)
ax.axis("off")
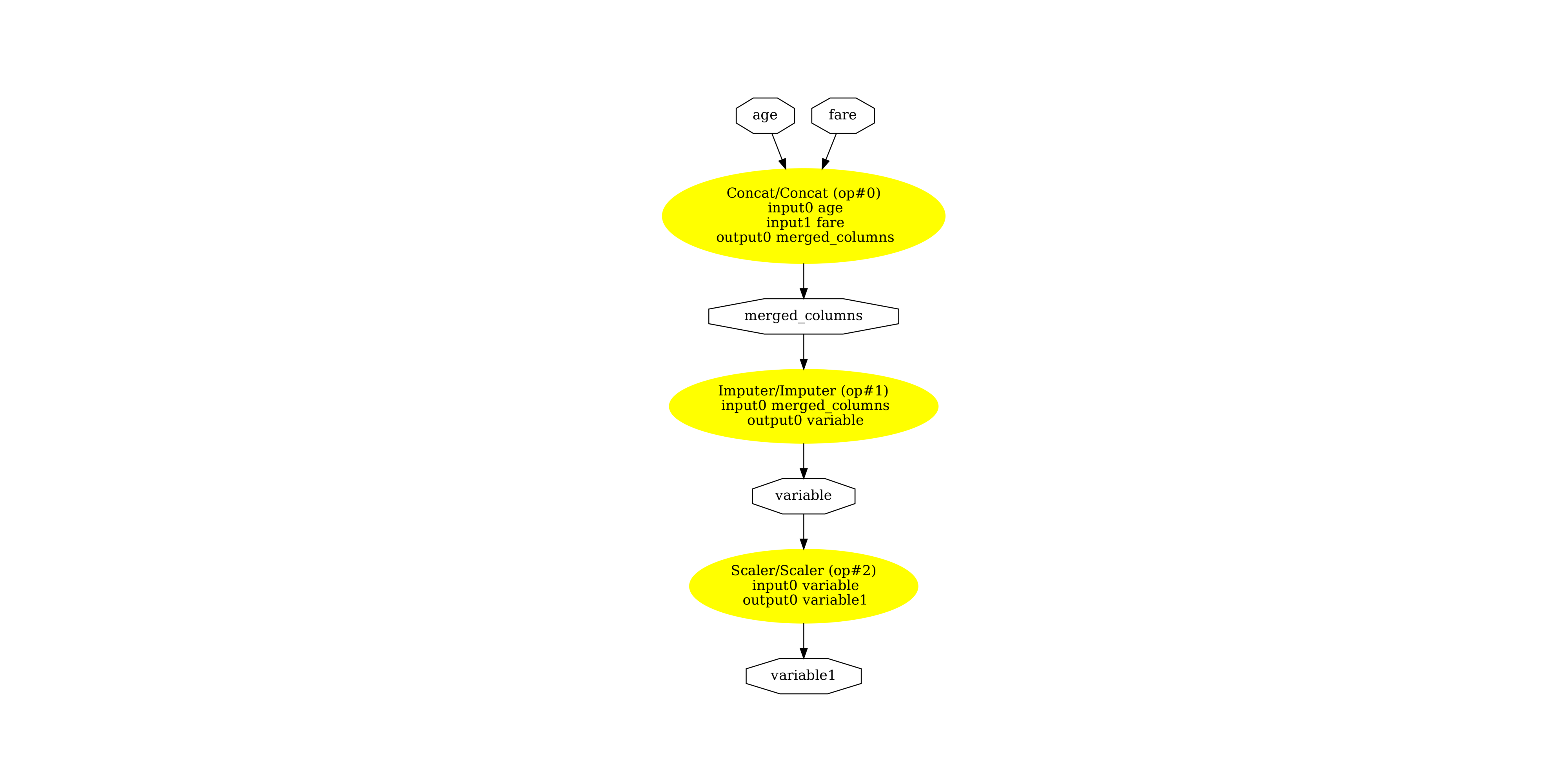
(np.float64(-0.5), np.float64(1229.5), np.float64(2558.5), np.float64(-0.5))
然后是文本管道。
pydot_graph = GetPydotGraph(
text_onnx.graph,
name=text_onnx.graph.name,
rankdir="TB",
node_producer=GetOpNodeProducer(
"docstring", color="yellow", fillcolor="yellow", style="filled"
),
)
pydot_graph.write_dot("pipeline_titanic_text.dot")
os.system("dot -O -Gdpi=300 -Tpng pipeline_titanic_text.dot")
image = plt.imread("pipeline_titanic_text.dot.png")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(40, 20))
ax.imshow(image)
ax.axis("off")
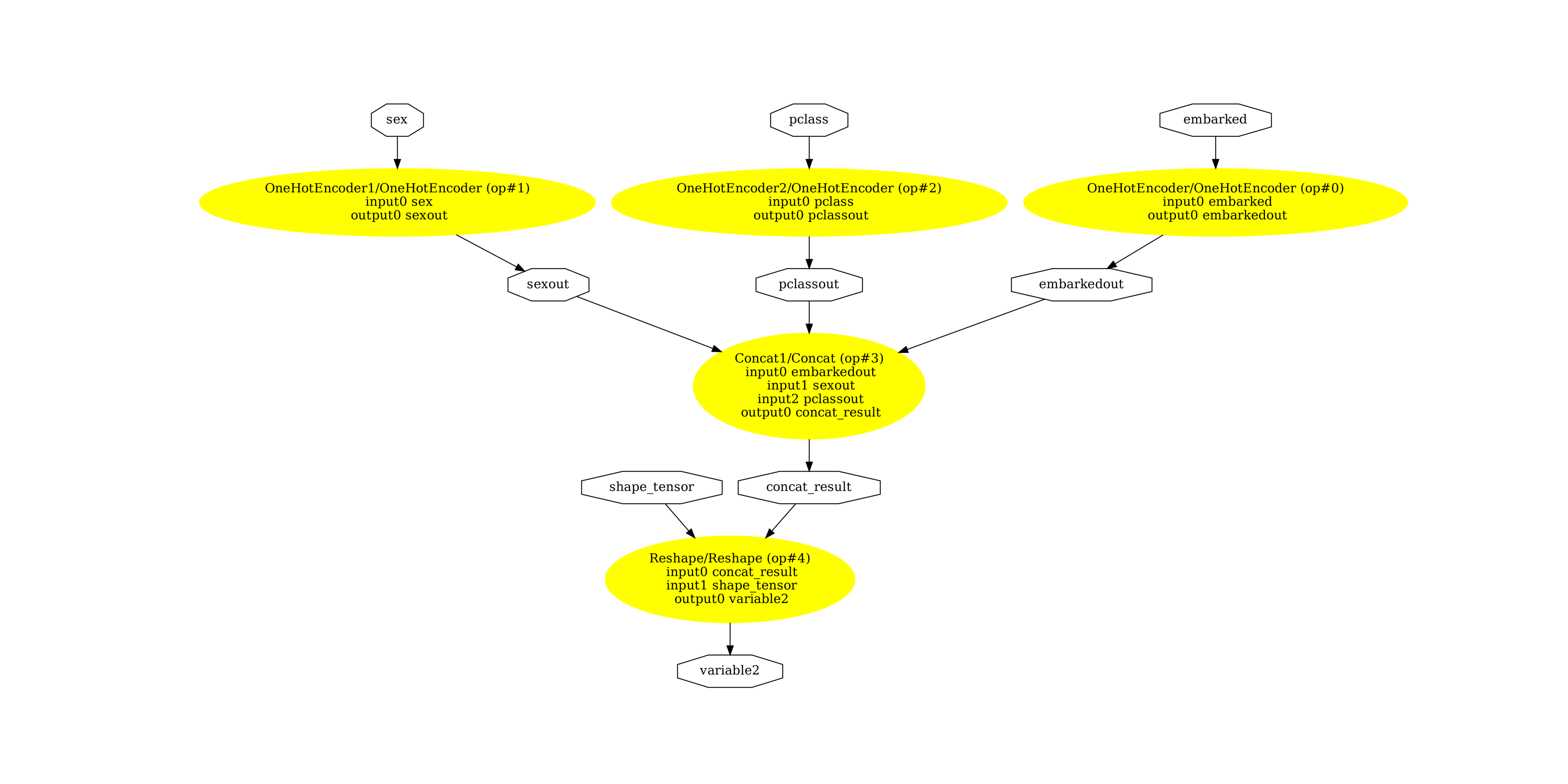
(np.float64(-0.5), np.float64(5630.5), np.float64(2735.5), np.float64(-0.5))
此示例使用的版本
print("numpy:", numpy.__version__)
print("scikit-learn:", sklearn.__version__)
print("onnx: ", onnx.__version__)
print("onnxruntime: ", rt.__version__)
print("skl2onnx: ", skl2onnx.__version__)
numpy: 2.3.1
scikit-learn: 1.6.1
onnx: 1.19.0
onnxruntime: 1.23.0
skl2onnx: 1.19.1
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 4.306 秒)