注意
转到末尾 下载完整的示例代码。
当自定义模型既不是分类器也不是回归器¶
scikit-learn 的 API 指定回归器产生一个输出,而分类器产生两个输出:预测标签和概率。这里的目标是增加第三个结果,用于指示概率是否高于给定阈值。这在 validate 方法中实现。
Iris 和评分¶
创建了一个新类,它训练任何分类器并实现了上述 validate 方法。
import inspect
import numpy as np
import skl2onnx
import onnx
import sklearn
from sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin, BaseEstimator, clone
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from skl2onnx import update_registered_converter
import os
from onnx.tools.net_drawer import GetPydotGraph, GetOpNodeProducer
import onnxruntime as rt
from skl2onnx.common._apply_operation import apply_identity, apply_cast, apply_greater
from skl2onnx import to_onnx, get_model_alias
from skl2onnx.proto import onnx_proto
from skl2onnx.common._registration import get_shape_calculator
from skl2onnx.common.data_types import FloatTensorType, Int64TensorType
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class ValidatorClassifier(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin):
def __init__(self, estimator=None, threshold=0.75):
ClassifierMixin.__init__(self)
BaseEstimator.__init__(self)
if estimator is None:
estimator = LogisticRegression(solver="liblinear")
self.estimator = estimator
self.threshold = threshold
def fit(self, X, y, sample_weight=None):
sig = inspect.signature(self.estimator.fit)
if "sample_weight" in sig.parameters:
self.estimator_ = clone(self.estimator).fit(
X, y, sample_weight=sample_weight
)
else:
self.estimator_ = clone(self.estimator).fit(X, y)
return self
def predict(self, X):
return self.estimator_.predict(X)
def predict_proba(self, X):
return self.estimator_.predict_proba(X)
def validate(self, X):
pred = self.predict_proba(X)
mx = pred.max(axis=1)
return (mx >= self.threshold) * 1
data = load_iris()
X, y = data.data, data.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
model = ValidatorClassifier()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
现在让我们衡量一下指示器,它告诉我们预测的概率是否高于阈值。
print(model.validate(X_test))
[0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0
1]
转换为 ONNX¶
新模型的转换失败,因为库不知道与此新模型关联的任何转换器。
try:
to_onnx(model, X_train[:1].astype(np.float32), target_opset=12)
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
Unable to find a shape calculator for type '<class '__main__.ValidatorClassifier'>'.
It usually means the pipeline being converted contains a
transformer or a predictor with no corresponding converter
implemented in sklearn-onnx. If the converted is implemented
in another library, you need to register
the converted so that it can be used by sklearn-onnx (function
update_registered_converter). If the model is not yet covered
by sklearn-onnx, you may raise an issue to
https://github.com/onnx/sklearn-onnx/issues
to get the converter implemented or even contribute to the
project. If the model is a custom model, a new converter must
be implemented. Examples can be found in the gallery.
自定义转换器¶
我们重用了 为自己的模型编写转换器 中的一些代码片段。形状计算器定义了转换模型每个输出的形状。
def validator_classifier_shape_calculator(operator):
input0 = operator.inputs[0] # inputs in ONNX graph
outputs = operator.outputs # outputs in ONNX graph
op = operator.raw_operator # scikit-learn model (mmust be fitted)
if len(outputs) != 3:
raise RuntimeError("3 outputs expected not {}.".format(len(outputs)))
N = input0.type.shape[0] # number of observations
C = op.estimator_.classes_.shape[0] # dimension of outputs
outputs[0].type = Int64TensorType([N]) # label
outputs[1].type = FloatTensorType([N, C]) # probabilities
outputs[2].type = Int64TensorType([C]) # validation
然后是转换器。
def validator_classifier_converter(scope, operator, container):
outputs = operator.outputs # outputs in ONNX graph
op = operator.raw_operator # scikit-learn model (mmust be fitted)
# We reuse existing converter and declare it
# as a local operator.
model = op.estimator_
alias = get_model_alias(type(model))
val_op = scope.declare_local_operator(alias, model)
val_op.inputs = operator.inputs
# We add an intermediate outputs.
val_label = scope.declare_local_variable("val_label", Int64TensorType())
val_prob = scope.declare_local_variable("val_prob", FloatTensorType())
val_op.outputs.append(val_label)
val_op.outputs.append(val_prob)
# We adjust the output of the submodel.
shape_calc = get_shape_calculator(alias)
shape_calc(val_op)
# We now handle the validation.
val_max = scope.get_unique_variable_name("val_max")
if container.target_opset >= 18:
axis_name = scope.get_unique_variable_name("axis")
container.add_initializer(axis_name, onnx_proto.TensorProto.INT64, [1], [1])
container.add_node(
"ReduceMax",
[val_prob.full_name, axis_name],
val_max,
name=scope.get_unique_operator_name("ReduceMax"),
keepdims=0,
)
else:
container.add_node(
"ReduceMax",
val_prob.full_name,
val_max,
name=scope.get_unique_operator_name("ReduceMax"),
axes=[1],
keepdims=0,
)
th_name = scope.get_unique_variable_name("threshold")
container.add_initializer(
th_name, onnx_proto.TensorProto.FLOAT, [1], [op.threshold]
)
val_bin = scope.get_unique_variable_name("val_bin")
apply_greater(scope, [val_max, th_name], val_bin, container)
val_val = scope.get_unique_variable_name("validate")
apply_cast(scope, val_bin, val_val, container, to=onnx_proto.TensorProto.INT64)
# We finally link the intermediate output to the shared converter.
apply_identity(scope, val_label.full_name, outputs[0].full_name, container)
apply_identity(scope, val_prob.full_name, outputs[1].full_name, container)
apply_identity(scope, val_val, outputs[2].full_name, container)
然后是注册。
update_registered_converter(
ValidatorClassifier,
"CustomValidatorClassifier",
validator_classifier_shape_calculator,
validator_classifier_converter,
)
然后是转换…
try:
to_onnx(model, X_test[:1].astype(np.float32), target_opset=12)
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
3 outputs expected not 2.
它失败了,因为库期望模型像一个产生两个输出的分类器一样运行。我们需要添加一个自定义解析器来告诉库这个模型产生三个输出。
自定义解析器¶
def validator_classifier_parser(scope, model, inputs, custom_parsers=None):
alias = get_model_alias(type(model))
this_operator = scope.declare_local_operator(alias, model)
# inputs
this_operator.inputs.append(inputs[0])
# outputs
val_label = scope.declare_local_variable("val_label", Int64TensorType())
val_prob = scope.declare_local_variable("val_prob", FloatTensorType())
val_val = scope.declare_local_variable("val_val", Int64TensorType())
this_operator.outputs.append(val_label)
this_operator.outputs.append(val_prob)
this_operator.outputs.append(val_val)
# end
return this_operator.outputs
注册。
update_registered_converter(
ValidatorClassifier,
"CustomValidatorClassifier",
validator_classifier_shape_calculator,
validator_classifier_converter,
parser=validator_classifier_parser,
)
再次转换。
model_onnx = to_onnx(model, X_test[:1].astype(np.float32), target_opset=12)
最终测试¶
现在我们需要检查 ONNX 的结果是否相同。
X32 = X_test[:5].astype(np.float32)
sess = rt.InferenceSession(
model_onnx.SerializeToString(), providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
results = sess.run(None, {"X": X32})
print("--labels--")
print("sklearn", model.predict(X32))
print("onnx", results[0])
print("--probabilities--")
print("sklearn", model.predict_proba(X32))
print("onnx", results[1])
print("--validation--")
print("sklearn", model.validate(X32))
print("onnx", results[2])
--labels--
sklearn [2 0 1 0 2]
onnx [2 0 1 0 2]
--probabilities--
sklearn [[3.53610536e-03 2.96349984e-01 7.00113911e-01]
[9.14084892e-01 8.58950540e-02 2.00538856e-05]
[2.89555721e-02 5.95367932e-01 3.75676496e-01]
[8.55410234e-01 1.44548971e-01 4.07951575e-05]
[1.20939795e-03 2.94797909e-01 7.03992693e-01]]
onnx [[3.5360949e-03 2.9634997e-01 7.0011395e-01]
[9.1408491e-01 8.5895061e-02 2.0050431e-05]
[2.8955542e-02 5.9536803e-01 3.7567648e-01]
[8.5541022e-01 1.4454898e-01 4.0807685e-05]
[1.2093951e-03 2.9479793e-01 7.0399266e-01]]
--validation--
sklearn [0 1 0 1 0]
onnx [0 1 0 1 0]
看起来不错。
显示 ONNX 图¶
pydot_graph = GetPydotGraph(
model_onnx.graph,
name=model_onnx.graph.name,
rankdir="TB",
node_producer=GetOpNodeProducer(
"docstring", color="yellow", fillcolor="yellow", style="filled"
),
)
pydot_graph.write_dot("validator_classifier.dot")
os.system("dot -O -Gdpi=300 -Tpng validator_classifier.dot")
image = plt.imread("validator_classifier.dot.png")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(40, 20))
ax.imshow(image)
ax.axis("off")
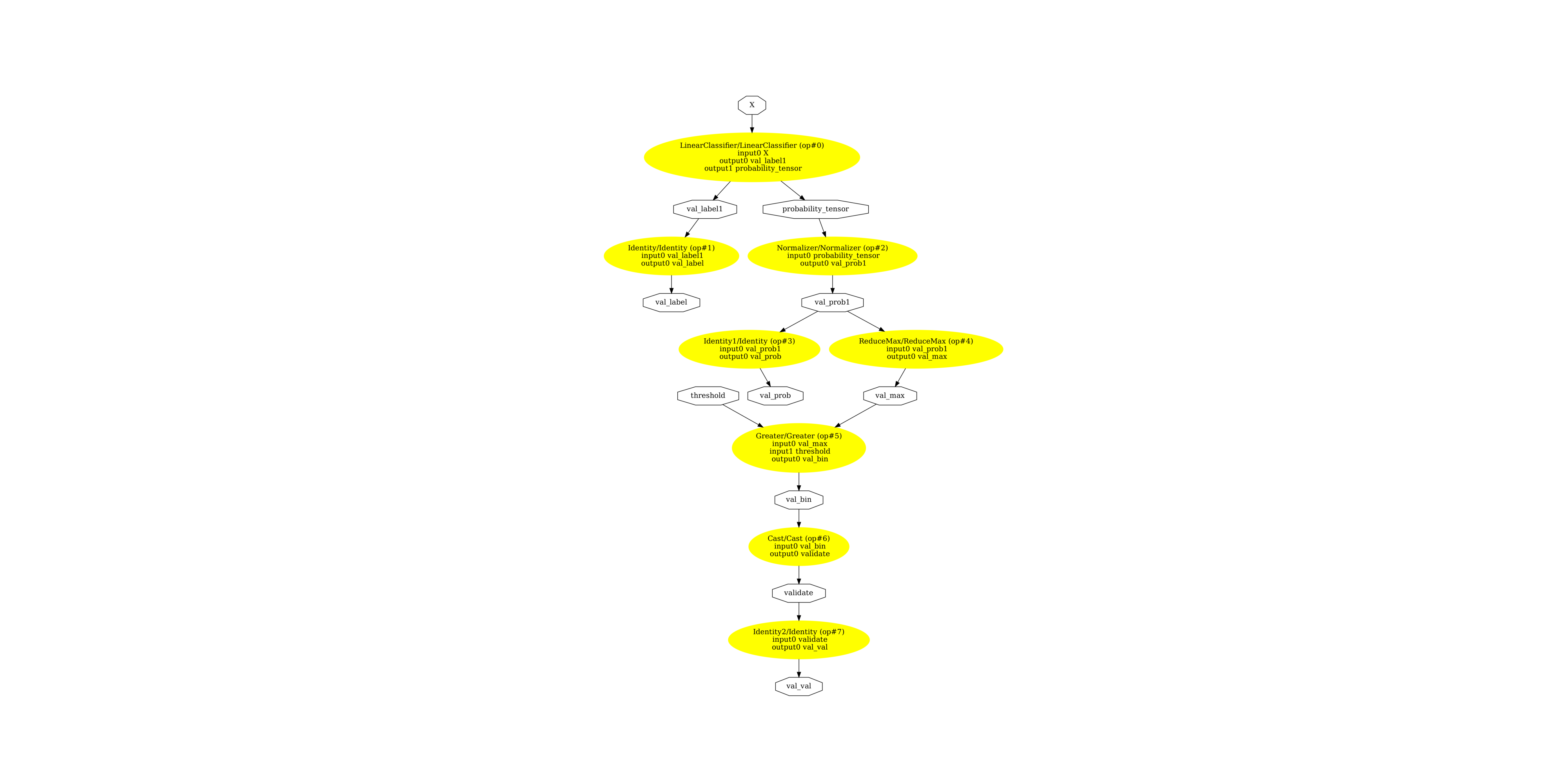
(np.float64(-0.5), np.float64(3293.5), np.float64(4934.5), np.float64(-0.5))
此示例使用的版本
print("numpy:", np.__version__)
print("scikit-learn:", sklearn.__version__)
print("onnx: ", onnx.__version__)
print("onnxruntime: ", rt.__version__)
print("skl2onnx: ", skl2onnx.__version__)
numpy: 2.3.1
scikit-learn: 1.6.1
onnx: 1.19.0
onnxruntime: 1.23.0
skl2onnx: 1.19.1
脚本总运行时间: (0 分 3.148 秒)